Chemical Residue Testing

Chemical Residue Testing
Though chemicals such as pesticides and sulfites are initially incorporated into commodities for reasons that may be beneficial, residues of such may compromise the health of consumers due to their toxicity or allergenic potential. As a result, the government either bans usage or regulates these substances to ensure that maximum allowable limits are not exceeded. Test kits offer rapid and accurate detection of these chemicals after a simple procedure validated for a variety of matrices.
The following are some of the common adulterants found in the food supply chain:
| Pesticide | Most crops are treated with pesticides. Pesticides enable farmers to increase crop yields, preserve product quality, and extend shelf life. However, pesticides can pose harmful effects upon exposure and ingestion. |
| GMO | Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) undergo a lot of biochemical processes with increasing GMO production around the globe, regulatory standards were established in order to facilitate trade and safety of GMO products for human consumption. |
| Meat and Bone Meal | Meat and bone meal is a valuable protein source in feed production. However, it was determined as the cause of the spread of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) or mad cow disease. In order to prevent the spread of BSE, most countries have imposed restrictions, and even outright bans, on the use of ruminant by-products and proteins in feed for ruminants. |
| Melamine | Melamine is a chemical used in a variety of industrial processes and can be found in food contact surfaces in processing plants, can coatings, dishware, and other kitchenware. Furthermore, it was also used illegally to increase the apparent protein content in food samples such as milk. |
| Sulfites | Sulfites are most often used as antimicrobial and antioxidant agents in food and beverages, particularly in wine-making during the fermentation process. Due to potential adverse reactions of intolerant individuals and other food safety concerns, total sulfite content is commonly regulated by government agencies to not exceed 10 ppm. |
| Methanol | Methanol is a highly flammable and poisonous liquid. Unscrupulous producers resort to intentionally adding methanol to alcoholic beverages as a cost-effective substitute for ethanol. Moreover, beverages rich in pectin, such as those derived from grapes and berries, can inadvertently lead to elevated levels of methanol during the fermentation process. In a proper and hygienic fermentation environment, methanol is produced at minimal and safe concentrations. However, when fermentation takes place under unsanitary conditions, methanol production can occur at higher levels. Methanol consumption, even in small amounts, can lead to severe health consequences, including blindness, organ failure, and death, to name a few. |
| Alkaline Phosphatase | An essential process in the production of safe and pathogen-free milk is pasteurization. Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme naturally present in all raw milk, but is destroyed during pasteurization. The Alkaline Phosphatase test is used by dairy farms and processors and food producers to determine whether milk has been sufficiently pasteurized, or whether it has been contaminated with raw milk after the process of pasteurization. |
Reagen™ Melamine ELISA Test Kit
Melamine ELISA Test Kit is a competitive enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative analysis of melamine in egg, milk, milk powder, infant formula, meat, fish, feed, chocolate yogurt, butter milk, sour milk and other food samples.
- Rapid results in less than 2 hours
- Cost-effective extraction method
- High sensitivity and low detection limit for liquid milk
- High reproducibility
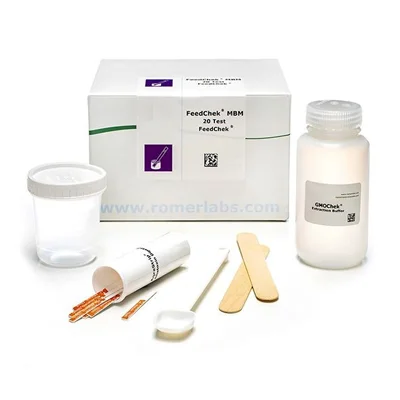
AgraStrip® FeedChek™ Meat and Bone Meal
The AgraStrip® FeedChek™ test kit for the detection of meat and bone meal (MBM) is designed to detect the presence of MBM in animal feedstuffs such as raw materials and finished feeds.
- User-friendly strip format
- Incorporates 2 tests into 1 test strip (mammalian and/or avian MBM, mammalian MBM).
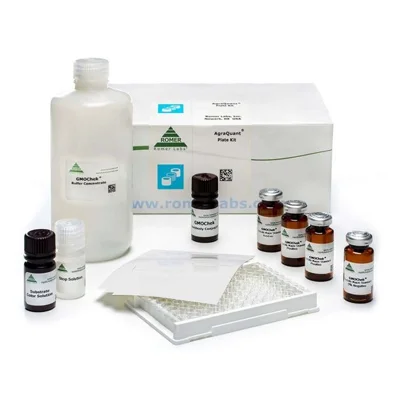
AgraQuant® GMOChek and SeedChek
AgraQuant® Test Kit is a sandwich-type enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) that quantitatively and qualitatively detects the GMO proteins in various raw and processed commodities. The kit can also be used to validate cleaning procedures or assay for trace allergens through rinse water or environmental swab.
- Rapid results in less than 2 hours
- Accurate and ready-to-use format
- Ideal solution for the simultaneous measurement of multiple samples with a result time of only 60 minutes
- Represents a simple, quantitative method that offers highly sensitive detection
- With highly purified antibodies for detection against proteins and fractions, making it an ideal solution for allergen control
- Detects proteins such as CP4 EPSPS, Bt-Cry1Ab, Bt-Cry1F, CP4 EPSPS, Vip3A, PMI, eCry3.1Ab, Bt-Cry1Ac, mEPSPS, Cry35
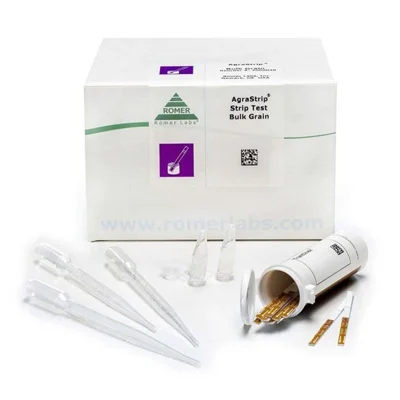
AgraStrip® GMO Test Kits TraitChek and SeedChek
AgraStrip® GMO strip test is a ready-to-use lateral flow device (LFD) for on-site testing that detects several proteins expressed in bulk grain, single seed and leaf samples for various commodities simultaneously in a quantitative and/or qualitative format.
- Accurate and ready-to-use format
- Suitable for on-site testing
- Rapid analysis of a wide range of commodities within only 6 minutes including extraction
- Results in as fast as 5 to 10 minutes including incubation time
- LOQ as low as 0.1% GMO in bulk grains
- Each kit includes either 100 single strips or 20 combs
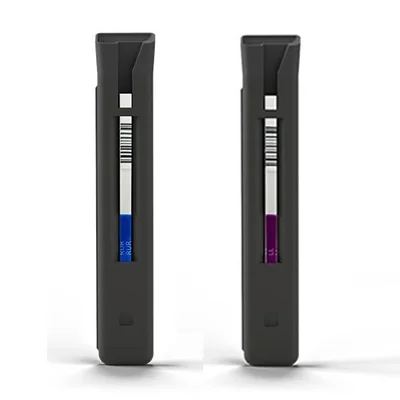
AgraStrip® PRO GMO Rapid Test Kits
AgraQuant® PRO GMO Lateral Flow devices enable the rapid, on-site quantification of the most common GM traits in corn, soy and canola
- Accurate and ready-to-use format
- Accurate and ready-to-use format
- Independent, simultaneous testing of up to four samples
- Limit of detection as low as 0.1%
- Intuitive and walk-away procedure
- Delivers quantitative results in easy-to-understand percentage format
- Manual timing and strip-cutting not necessary
- AgraStrip Pro RUR Bulk Grain features LOD of 0.05% in high-sensitive method that quantifies CP4 EPSPS in soy
- AgraStrip Pro LL Bulk Grain quantifies PAT in soy, corn and canola
Glenwood offers the solution for chemical residue testing—a wide range of Lateral flow formats and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) test kits that are both available to cater to the continuously growing demands in the food and feed industries. From qualitative to quantitative testing, reliable and accurate results can be obtained in the shortest possible time for various commodities. Be our partner today and ensure your safety from risky chemicals.